How To Configure Tunneling on Cisco Packet Tracert
Definition of Tunneling
Tunneling is the basis of VPN to create a private network through the Internet. Tunneling is also the encapsulation or packaging of a protocol into a protocol packet.
Tunneling provides a connection point-to-point logical along the connectionless IP network. The process of transferring data from one network to another network utilizing the Internet as a veiled (tunneling). When the package runs menujun to the destination node, these packets through a pathway called tunnel.
Called tunnel because applications that use only saw two end points, so the package through the tunnel will only do one leap or hop. Tunneling on the VPN uses encryption to protect the data to not be seen by parties not authorized and to make a multiprotocol encapsulation if necessary.
Tunneling is a method to transfer data from one network to another network using the Internet underground. Protocol tunneling does not transmit the frame as generated by the nodes of origin for granted, but wrapping it shortly encapsulation in an additional header. The additional header provides routing information so that data can pass through the frame sent.
TOPOLOGI
Tool :
1. Router 1941 3 pieces
2. Switch 2960-24TT 2 pieces
3. PC 2 pieces
4. Router used gigabyte ethernet port
Step :
1. Create a topology like the picture above
2. Port on IP 11.11.11.1/24 MUST USED ETHERNET Gigabyet 0/1
3. Port pada IP 12.12.12.2/24 MUST USED M ETHERNET Gigabyet 0/1
4. Beri IP pada setiap PC
5. Setting router 2 sebagai berikut :
Router>enable (to turn on the router)
Router#configure terminal (to configure the router)
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#interface gig0/0 (to set interface gigabitethernet0/0)
Router(config-if)#ip address 10.10.10.10 255.255.255.0 (to give ip on port gig0/0)
Router(config-if)#no shutdown (to turn on the port)
Router(config-if)#
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface GigabitEthernet0/0, changed state to up
%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface GigabitEthernet0/0, changed state to up
Router(config-if)#interface gig0/1
Router(config-if)#ip add 11.11.11.1 255.255.255.0
Router(config-if)#no shutdown
Router(config-if)#
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface GigabitEthernet0/1, changed state to up
Router(config-if)#interface tunn0 (to set interface tunnel 0)
Router(config-if)#
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface Tunnel0, changed state to up
Router(config-if)#ip address 172.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
Router(config-if)#tunnel source g0/1 (to set source of interface tunnel)
Router(config-if)#tunnel destination 12.12.12.2 (to set the destination of interface tunnel)
Router(config-if)#tunnel mode gre ip (to set mode tunnel)
Router(config-if)#exit ( to exit from configure)
Router(config)#ip route 13.13.13.0 255.255.255.0 172.168.1.2 (makes routing to the destination LAN)
Router(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 gig0/1 (give a default route via ethernet)
%Default route without gateway, if not a point-to-point interface, may impact performance
Router(config)#
6. Setting router 1 (no routing)
Router>en
Router#config t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#int g0/0
Router(config-if)#ip add 11.11.11.2 255.255.255.0
Router(config-if)#no sh
Router(config-if)#
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface GigabitEthernet0/0, changed state to up
%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface GigabitEthernet0/0, changed state to up
Router(config-if)#int g0/1
Router(config-if)#ip add 12.12.12.1 255.255.255.0
Router(config-if)#no shut
Router(config-if)#
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface GigabitEthernet0/1, changed state to up
Router(config-if)#
7. Setting router 3
Router>en
Router#config t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#int g0/0
Router(config-if)#ip add 13.13.13.10 255.255.255.0
Router(config-if)#no shut
Router(config-if)#
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface GigabitEthernet0/0, changed state to up
%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface GigabitEthernet0/0, changed state to up
Router(config-if)#int g0/1
Router(config-if)#ip add 12.12.12.2 255.255.255.0
Router(config-if)#no sh
Router(config-if)#
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface GigabitEthernet0/1, changed state to up
%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface GigabitEthernet0/1, changed state to up
Router(config-if)#int tunn0
Router(config-if)#
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface Tunnel0, changed state to up
Router(config-if)#ip add 172.168.1.2 255.255.255.0
Router(config-if)#tunn source g0/1
Router(config-if)#tunn destination 11.11.11.1
Router(config-if)#ex
Router(config)#ip route 10.10.10.0 255.255.255.0 172.168.1.1
Router(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 gigabitethernet 0/1
%Default route without gateway, if not a point-to-point interface, may impact performance
Router(config)#
%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Tunnel0, changed state to up
Router(config)#
8. Please try to test ping from PC1 to PC2
Then test with tracert in cmd PC
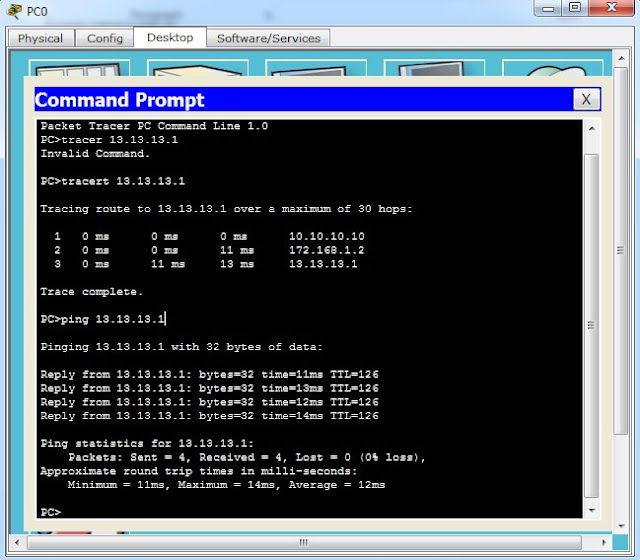
Packages have successfully passed Tunnel
Then test with tracert in cmd PC

Packages have successfully passed Tunnel
Hope it is useful
if there are not clear, please ask in the comments
Have a good study :)
if there are not clear, please ask in the comments
Have a good study :)

















0 komentar:
Posting Komentar